Fetching remote branches
The changes from the remote branch automatically merge into your current local branch when executing a pull as long as there are no conflicts. If you want to obtain the remote changes but not have them merged into your current local branch, you can execute the git fetch command.
Fetch will download changes from the remote that do not yet exist on your local branch. TheFETCH_HEAD ref will track the fetched changes from the remote repository.
When both the remote and local branches contain different descendants, the revision history will look like this:
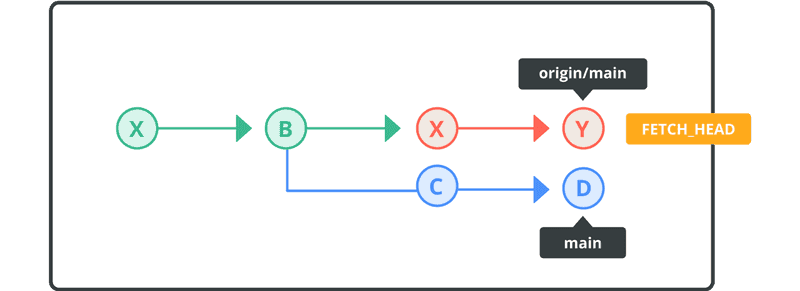
Once changes are fetched, you can apply those changes to your local repository by merging in FETCH_HEAD or executing a pull.
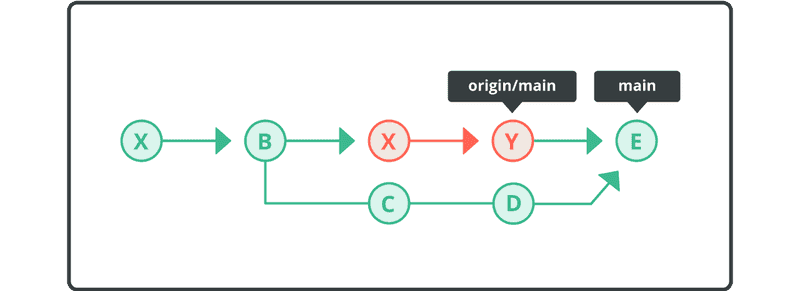
Once FETCH_HEAD has merged, the revision history will yield the same result as a git pull operation. Pull is a simultaneous execution of fetch and merge operations.
Best practices for fetching remote branches
- Fetch Regularly: Regularly fetching updates ensures that you are aware of the latest changes made by your collaborators. This helps in staying informed about new commits, branches, and changes.
- Review before integrating: After fetching, review the changes and commits before merging them into your local branches. This helps you understand what has changed and plan how to integrate those changes.
- Use branch names: Fetch updates for specific branches to minimize the data transferred and focus on relevant changes.
- Avoid fetching and merging together: Use
git fetchandgit mergeas separate commands instead ofgit pullto have more control over the process. This allows you to review changes before merging. - Use fetch to sync tags: Fetching also updates your local copy of the remote tags. Use
--tagsto ensure all tags are fetched. - Handle conflicts carefully: Be prepared to handle conflicts that may arise when you merge fetched changes. Carefully resolve conflicts to ensure a smooth integration.
- Fetch all remotes: If your repository has multiple remotes (e.g., origin and upstream), fetch updates from all remotes to stay synchronized.
- Clean up after fetching: Use the
--pruneoption to remove references to branches that have been deleted in the remote repository. This keeps your local repository clean and up-to-date. - Automate fetching: Set up automated tasks or hooks to fetch updates regularly. This can be done using cron jobs or by integrating fetching into your development workflow tools.